- VENC settings:
- Optimal within 25% of the true peak velocity
- Too low: flow aliasing
- Too high: underestimating velocity
- Correct direction of flow (R-L, F-H)
- Image plane distal from valve leaflet tips
- Flow assessment: perpendicular to the vessel
- Max. velocity assessment: perpendicular to the jet
- Avoid underestimation of velocities. Check:
- Adequate temporal resolution (phases)
- Free-breathing acquisition: 30 phases
- Breath-hold acquisition: 20-25 phases
- Rotate FOV - orthogonal to the direction of flow
- Slice thickness: <7mm
- For correct planning see "Standard Views"
|
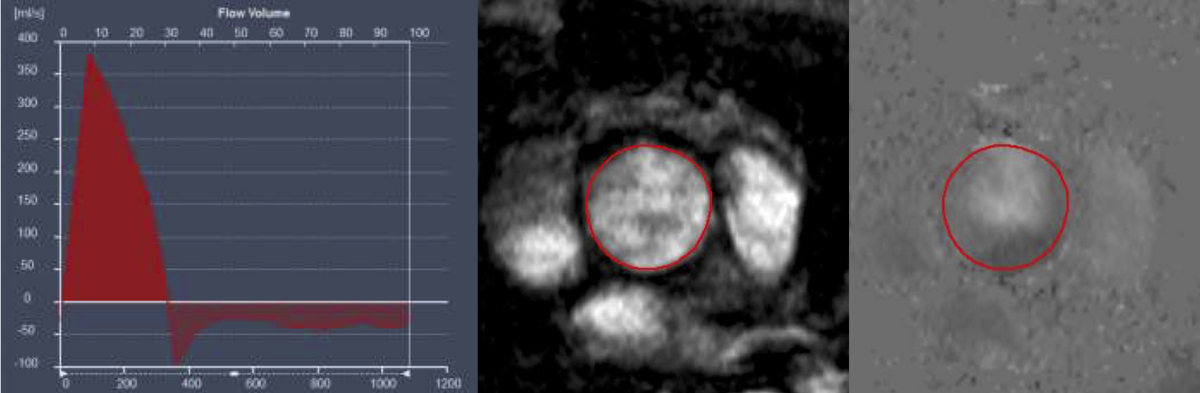 Volume time curve from flow velocity encoding through the ascending aorta in a patient with severe aortic regurgitation
Volume time curve from flow velocity encoding through the ascending aorta in a patient with severe aortic regurgitation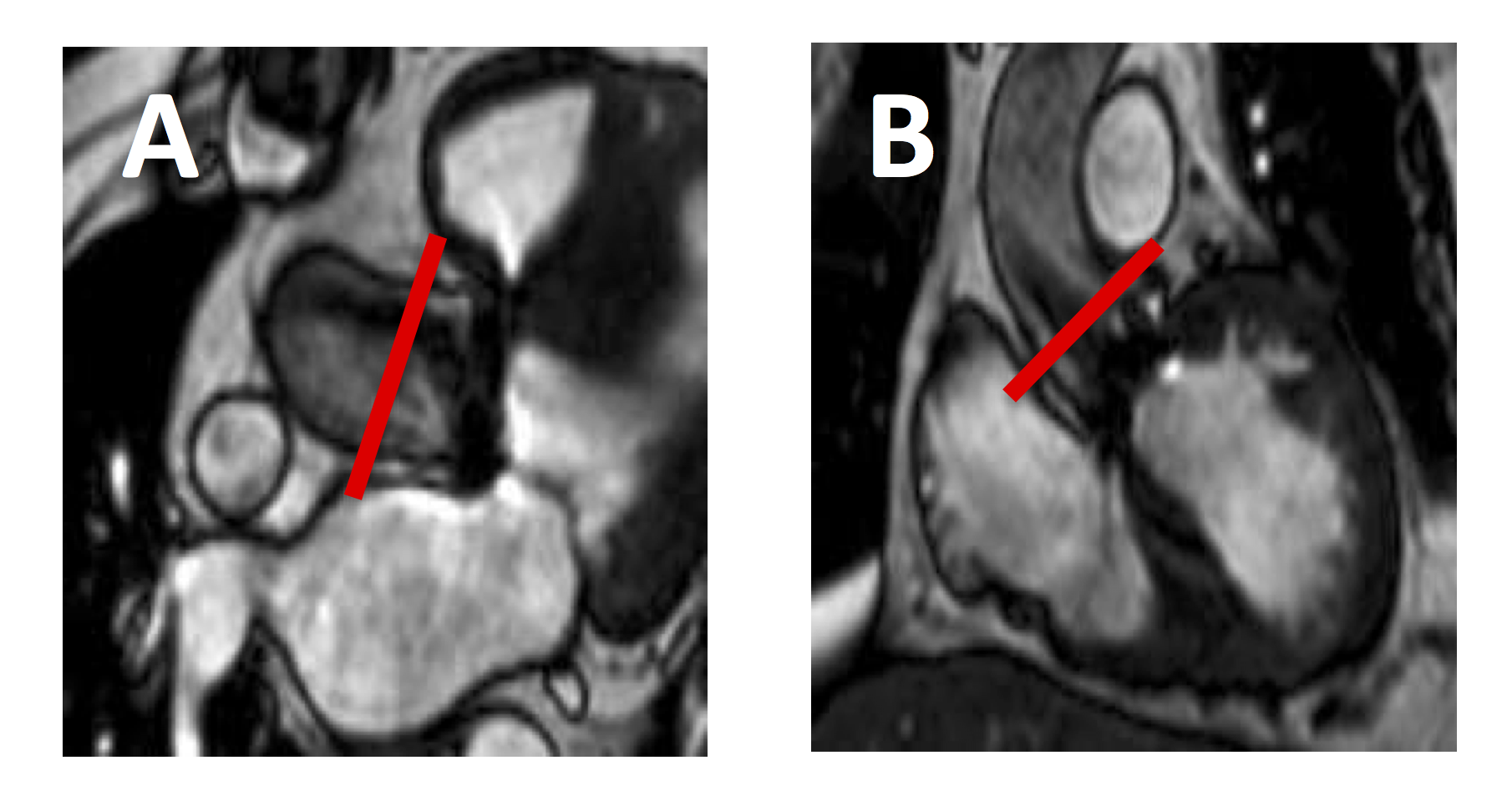 Sagittal (A) and coronal (B) slice positioning for aortic stenosis
Sagittal (A) and coronal (B) slice positioning for aortic stenosis