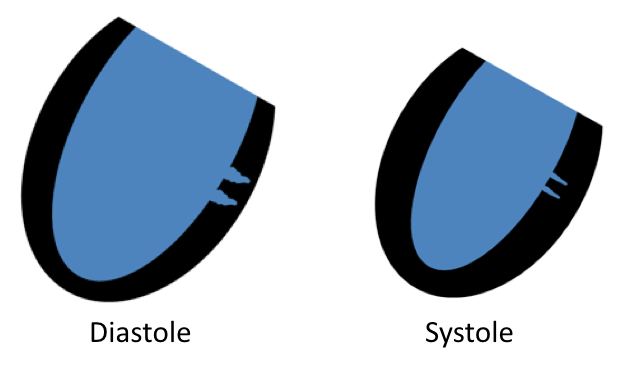
| LV Crypt (congenital) |
|
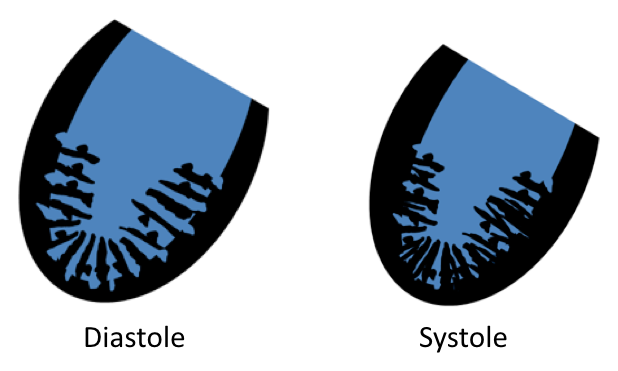
| LV Non-Compaction (congenital) |
|
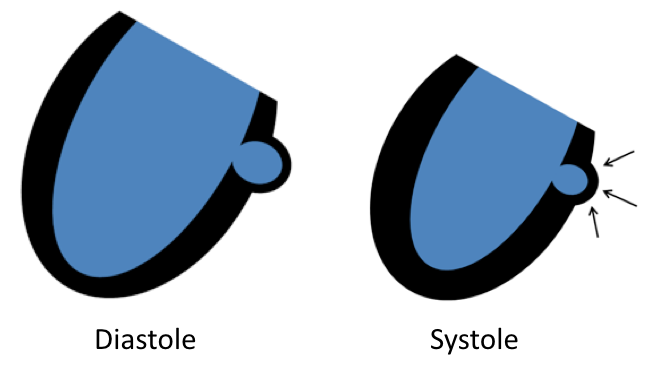
| Diverticulum (congenital) |
|
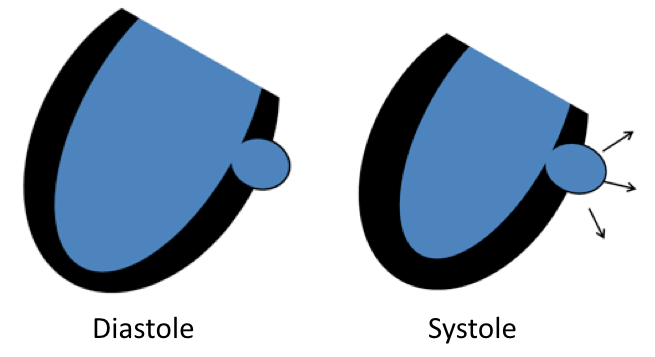
| True aneurysm (infarction, congenital) |
|
| Pseudoaneurysm (infarction, trauma) |
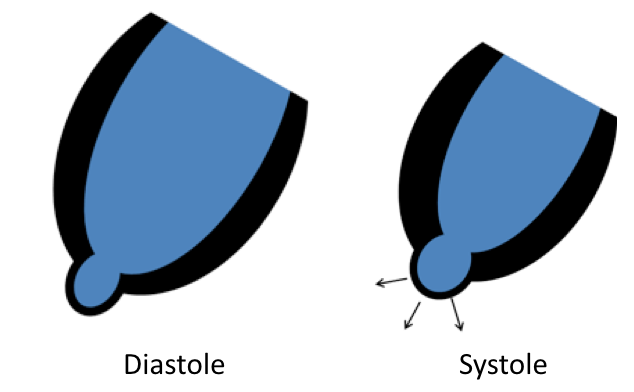
|