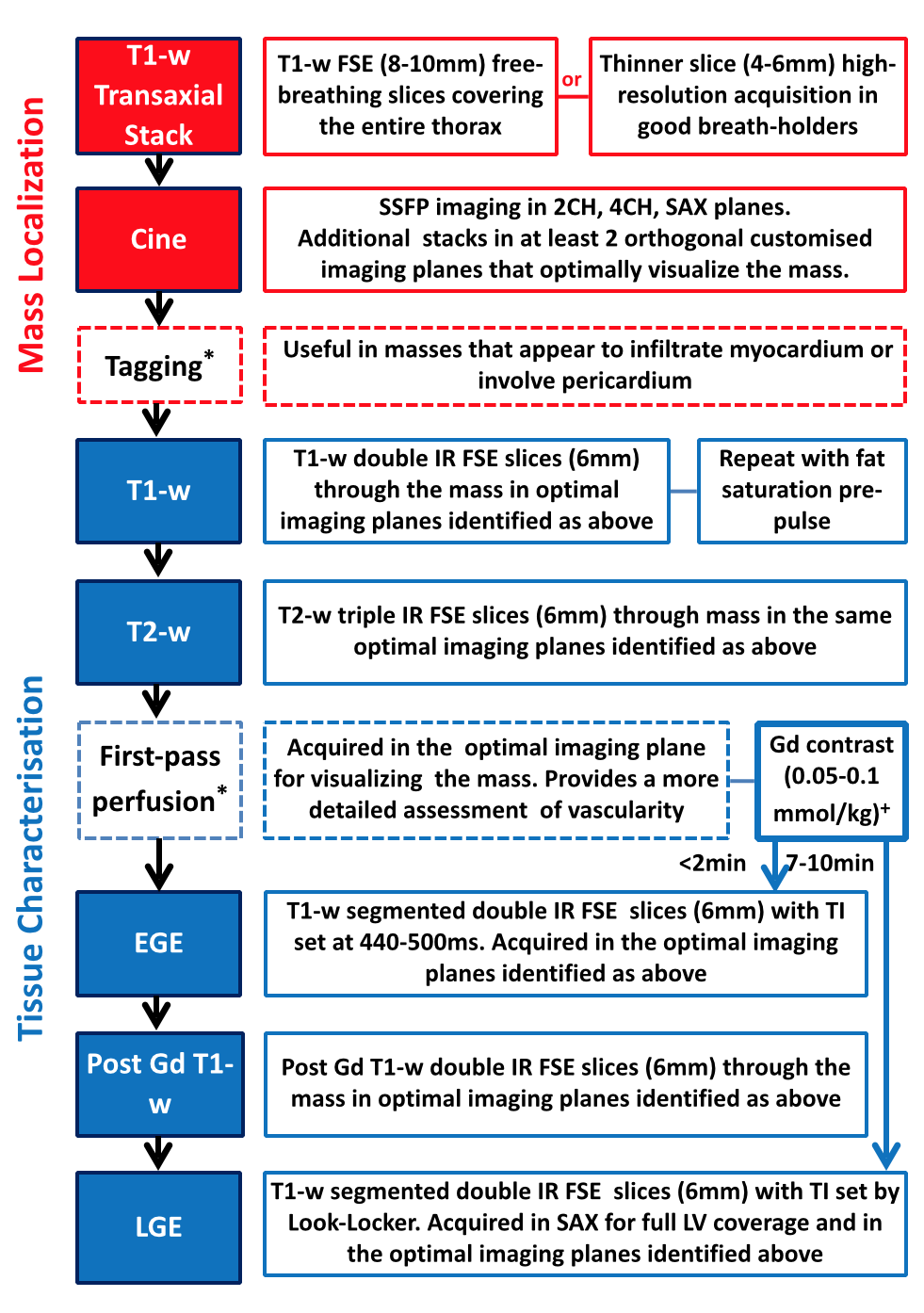
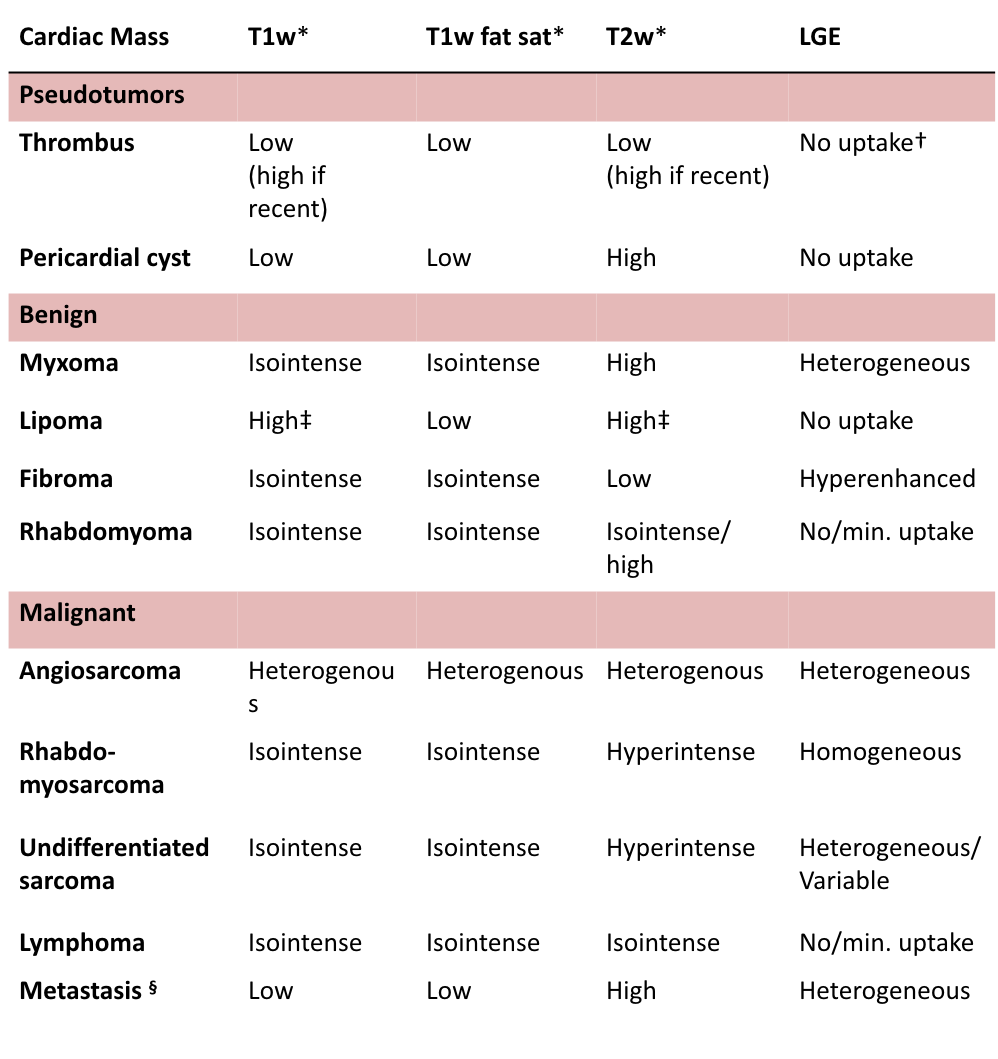
- Cardiac metastatic lesions are up to 1000 times more common than primary tumours
- Common sources of metastic lesions
- Melanoma, thyroid cancer, breast cancer, renal carcinoma, soft tissue carcinoma, lung cancer, esophageal cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma
- Common benign primary tumours (70%)
- Myxoma, lipoma, fibroelastoma, fibroma, rhabdomyoma,
hemangioma
- Common malignant primary tumours (30%)
- Angiosarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, mesothelioma, fibrosarcoma, lymphoma
- Typical tumour locations*:
- Any chamber: Lipoma (intramural / intracavitary ), Hemangioma (intracavitary), Rhabdomyosarcoma (intramural, metastases).
- Ventricles: Fibroma (intramural), Rhybdomyoma (intramural).
- Valvular: Fibroelastoma, Vegetations.
- Left Atrium: Thrombus, Myxoma, Fibrosarcoma, Osteosarcoma, Leiomyosarcoma (posterior wall), undiffertiated sarcoma.
- Right Atrium: Angiosarcoma, Lymphoma.
- Pericardium: Pericardial cyst, metastases.
- Consider pseudo tumours:
- Normal heart structures, thrombus, cyst or vegetation
|